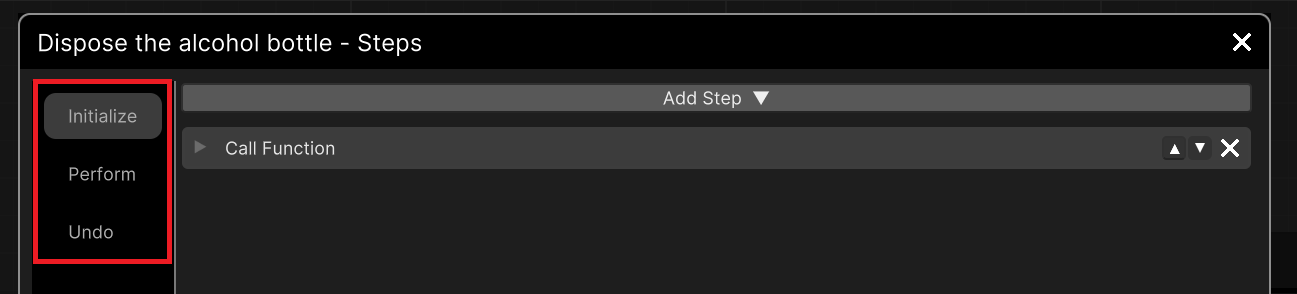
Scenegraph Steps¶
Scenegraph Steps is an easy way to add more functionality to your Actions. With Steps you can set behaviors like spawning, destroying, call functions and send messages from the Actions without writing any code. The Steps are attached into a specific time-frame within the Action (during Initialize, Perform or Undo) and invoke when its time.
Hint
Scenegraph Steps enhance the no-code editor with a powerful tool, ideal for customizations.
How to open¶
To open the Steps panel, click on the “lighting” icon on the top right side of an Action node.
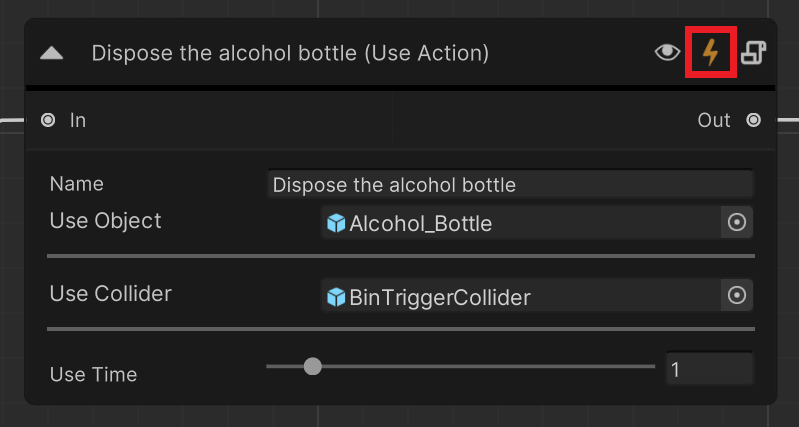
Main panel¶
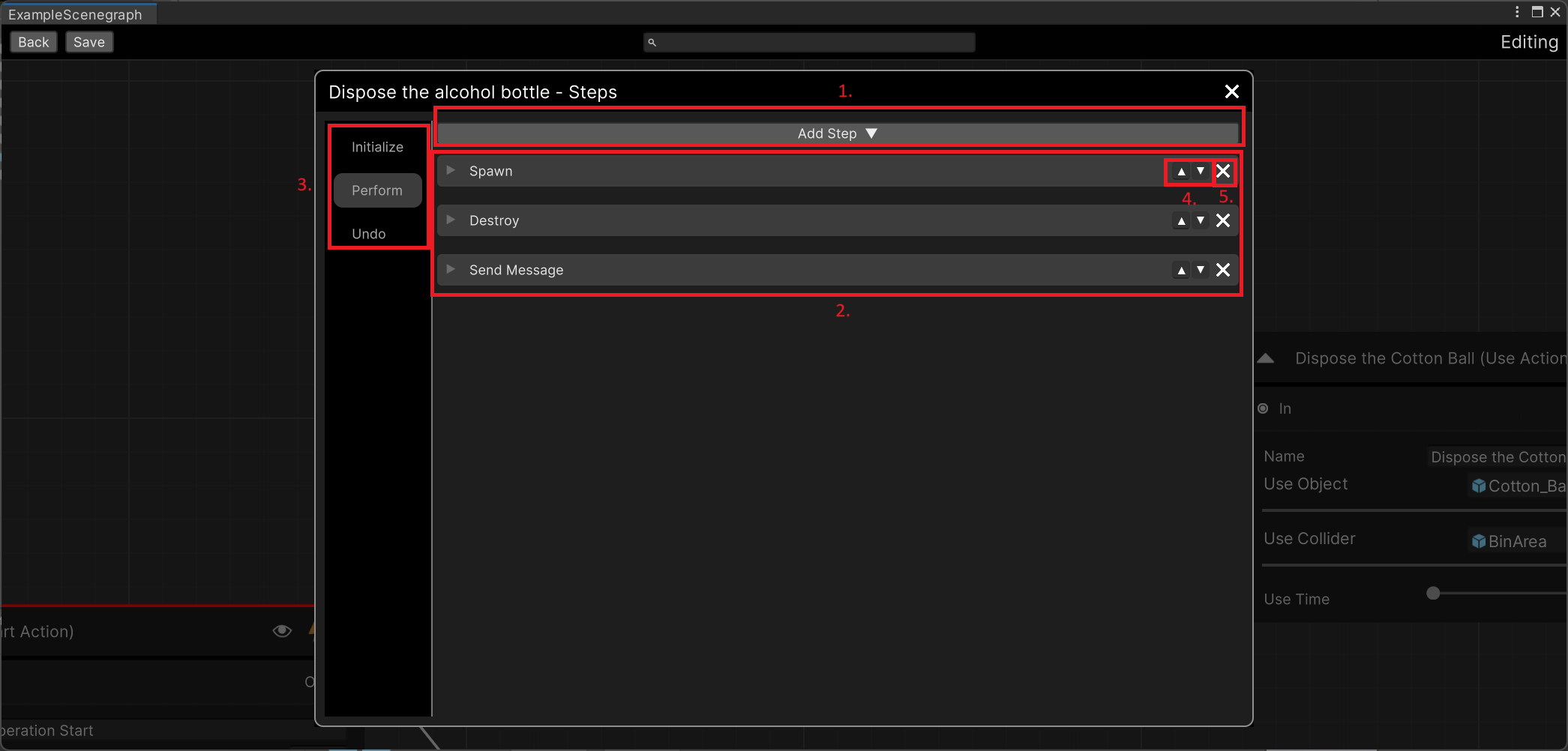
This is the Steps panel.
Feature ID |
Explanation |
|---|---|
1 |
To add a Step, press the “Add Step” dropdown button and select the Step you need. |
2 |
Those are the available Steps for this particular Action |
3 |
A Step is invoked on a specific point during the Action. From this panel on the left you can set when the Step will be triggered, you can select between Initialize (at the beginning of the Action) , Perform (when the Action is completed) and Undo (when from this Action we go to the previous one). |
4 |
To change the order of the Steps. Press the up and down arrow icons to change them. This also defines the invoking order. |
5 |
To delete a Step, press the “x” button on the right side of the Step. |
Add Step panel¶
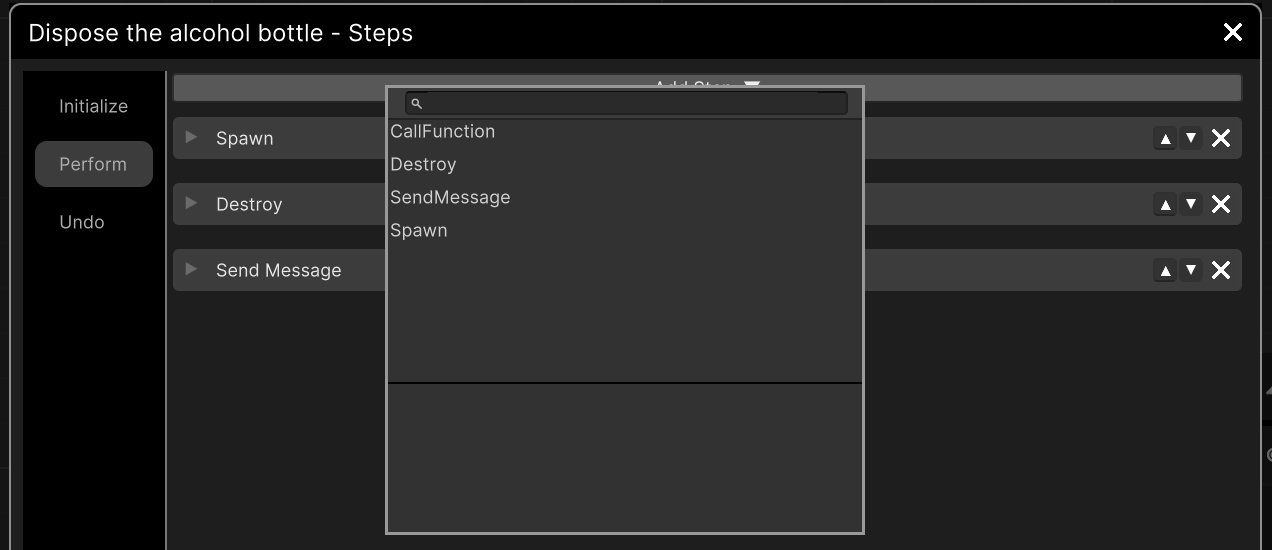
This panel shows the available Steps for the Action.
Parameter name |
Explanation |
|---|---|
CallFunction |
With this Step you can call a custom function. |
Destroy |
Destroy an object from the scene. |
SendMessage |
Send a message by invoking a function from an object |
Spawn |
Spawn an object from your assets. |
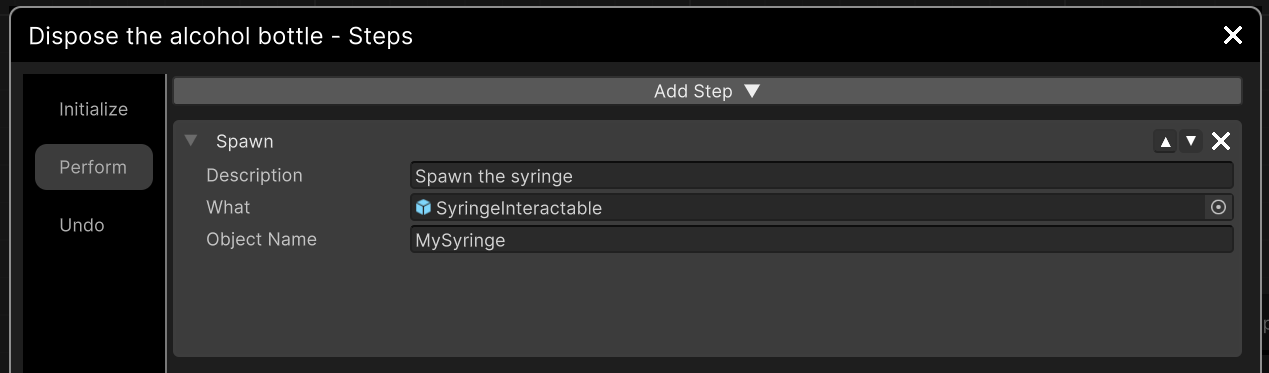
Spawn Step¶
With this Step you can spawn an object to your scene.
Hint
This is used in cases where you want to spawn additional objects in your Actions.
Parameter name |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Description |
Set a name to your Step. |
What |
Drag and drop a prefab from the assets in this field. It will be spawned to the scene when the Step is triggered. |
Object Name |
Set a name to override the spawned object’s name. |
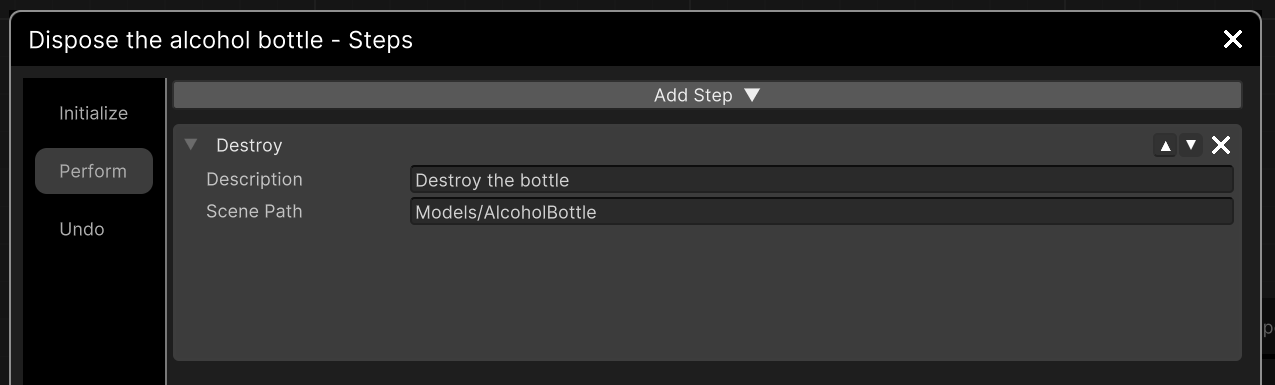
Destroy Step¶
Destroy an object from the scene.
Parameter name |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Description |
Set a name to your Step. |
Scene Path |
Give a scene path to the object you want to destroy. Works in the same way as the |
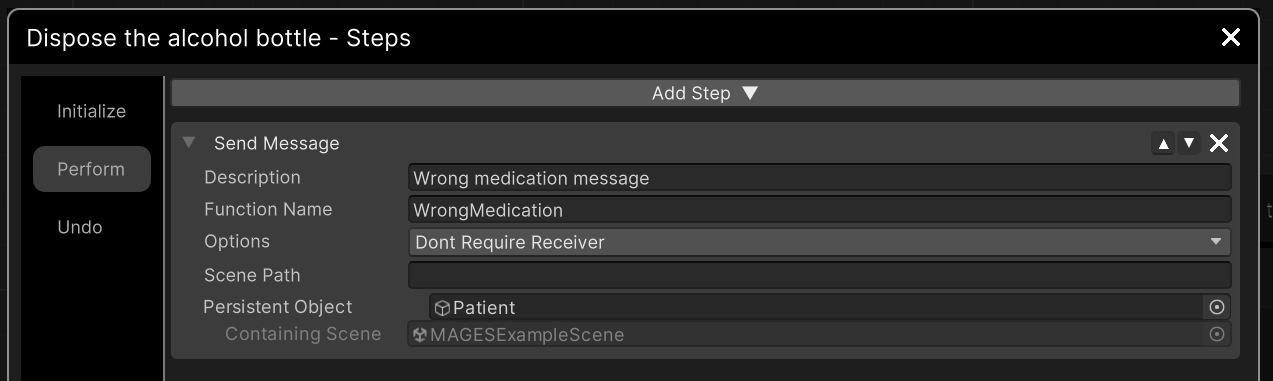
Send Message Step¶
Broadcasts a message using Unity’s Broadcast Message.
Parameter name |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Description |
Set a name to your Step. |
Function Name |
This is a public function that will be broadcasted through the message. This method should be implemented in a script that is attached to the Persistent object or the object from the Scene path. |
Options |
Set if the message requires a receiver or not. If you set it to require and then no one receives the message an Error will be thrown. |
Scene Path |
Give a scene path to the object you want to destroy. Works in the same way as the |
Persistent Object |
This is another alternative to the scene path setup. Just drag and drop the object you want from the scene to keep its reference. |
Warning
Remember that the Function Name should be a public method in a script that is attached to the object (configured from the path or the reference).
Call Function Step¶
Calls a function from a script that is attached to an object.
Parameter name |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Description |
Set a name to your Step. |
Is Scene Object |
If set to yes you will specify your object by reference, otherwise you will set its full scene path manually. |
Scene Object Reference |
This is another alternative to the scene path setup. Just drag and drop the object you want from the scene to keep its reference. |
Type |
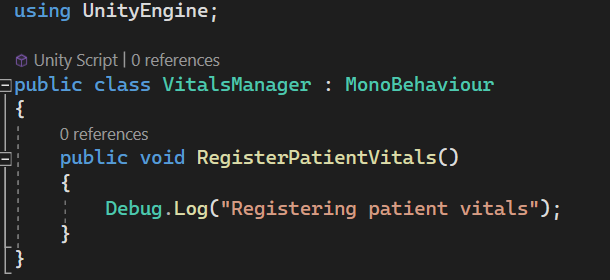
Dropdown showing the public functions of the attached script. Select the function you want to invoke. |
This is the method that will be invoked in the example above.
Hint
Call Function Steps are very useful to call external functions that are attached to other objects without writing any additional code.
When to invoke the Steps¶
On the left side of the screen, you can set when each Step will run. You have 3 different options.
Configure Steps that run on the
Initialize()of each Action (after the initialization)Run the Step after the
Perform()method.Upon
Undo(). This is called when you are in the Action and you go to the previous one.